On a clear night, it is possible to see more than 3,000 stars with the naked eye. There are billions of other stars up there in the sky, but we cannot see them.
The nighttime sky holds clues about the life and death of stars. These clues are found in fuzzy-looking clouds of glowing gas sprinkled with black dust. These clouds are called nebulae (NEB-u-lie). The word nebula (singular form of nebulae) comes from the Latin word for cloud. When viewed through a low-power telescope, nebulae look like cotton balls. But high-power telescopes show that nebulae are huge multishaped, multicolored structures. Some nebulae signal the birth of stars, while others are relics from the death of stars.

▲ How Stars Burn
A star is a burning mass of gas held together by its own gravity. It uses the lightest element, hydrogen, for fuel. Hydrogen atoms have one proton each. Energy is released when two hydrogen atoms join together to form a heavier atom called helium, which has two protons. When the two hydrogen atoms combine, some of their mass becomes a huge burst of energy.
Stars Need Fuel
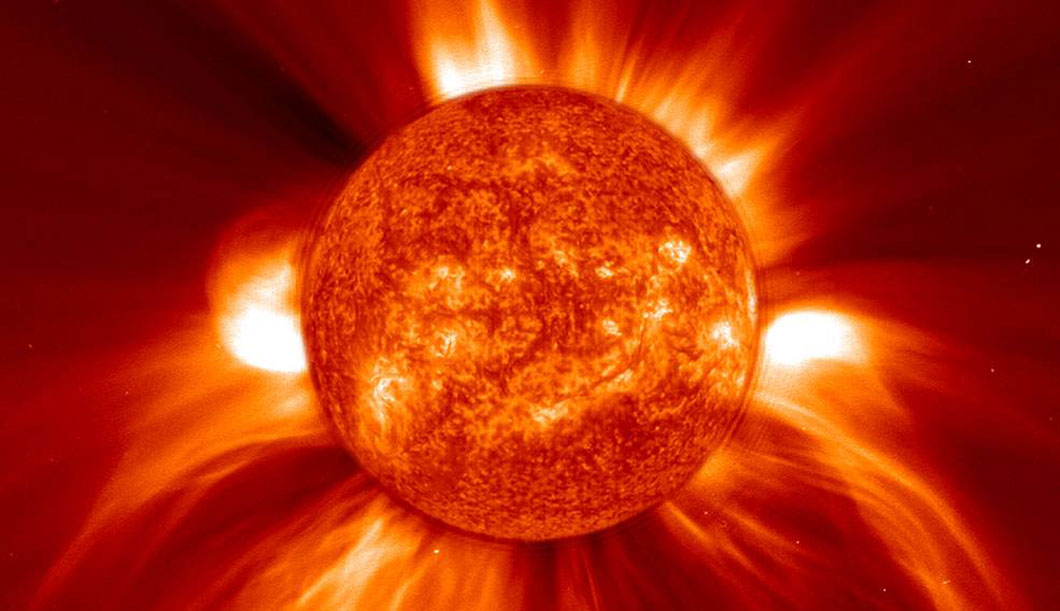
▲ To create energy, stars need fuel—and when that fuel is used up, the star fades. Stars that weigh more than the Sun (above) burn out quickly and even explode. Our Sun will not burn out for another 5 billion years.
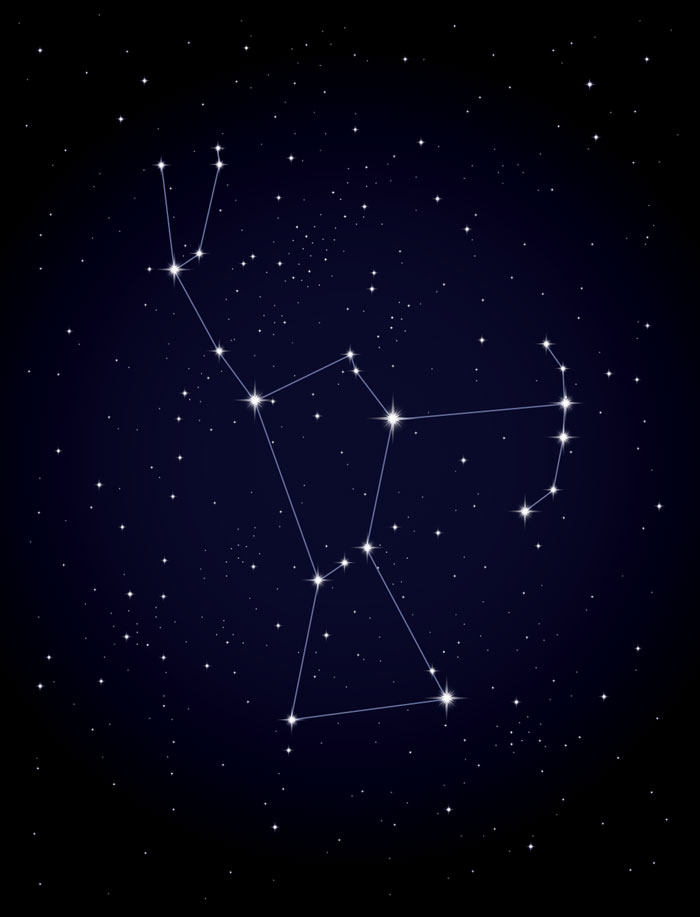


◀ Mapping Where Stars Are
To help find their way around the sky, astronomers subdivide it into 88 regions, like counties in a state. The regions correspond to imaginary stick-figure pictures called the constellations. Many cultures have their own set of legendary sky figures. We use the mythological characters imagined by the ancient Greeks and ancient Egyptians. Orion, the Hunter, is one of the most recognizable constellations, because his shoulders, legs, and waist are easy to trace.

▲ Light-Years Away
Stars are much farther away from Earth than the planets are. Our Sun is 93 million miles away. Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Sun, is 24 trillion miles away from it. Because numbers in the trillions include so many zeros, scientists use light-years to measure such great distances. A light-year is the distance a beam of light travels in a year (nearly 6 trillion miles). A beam of light takes 1.3 seconds to travel between the Moon and Earth, and 8.3 minutes to travel the 93 million miles between the Sun and Earth. Stars are too far away to visit with spacecraft, so we need powerful telescopes to view them.
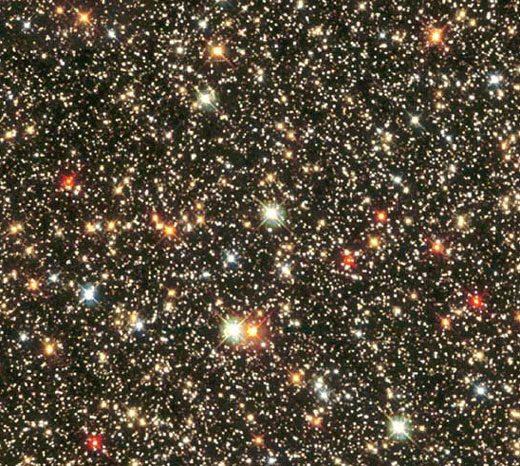
Jewel Box of Stars
This is a telescopic view looking into the dense heart of our galaxy. It shows that stars come in many colors. Most blue stars are young and hot, up to ten times hotter than our Sun, while red stars are cooler, only half the Sun’s temperature. ▶








