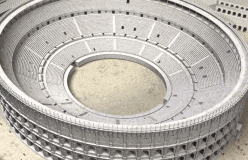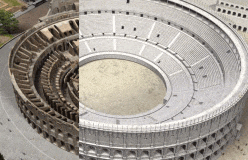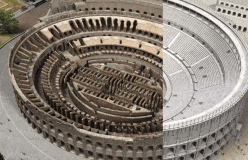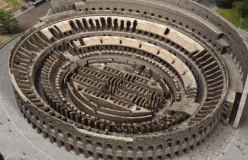
The rich lived, dressed, and even ate differently from the poor. In the city, rich Romans built their town houses as far as possible from the noisy, narrow streets of the poor.
Although from the outside their homes often looked plain, inside they were costly and comfortable, with sunny courtyards, pools, and gardens. The rich filled their houses with furniture made of bronze, ivory, and rare wood. Brightly painted walls were decorated with murals. Many wealthy Romans also had huge country estates called villas.
Only the children of the rich got a formal education. They started school at about age 6, and most left school by age 12. Boys and girls attended separate schools. Girls finished their schooling before boys and began preparing for marriage. Some boys continued their education and became the empire’s leading citizens. At 14, Roman boys took part in a special ceremony marking the end of childhood.