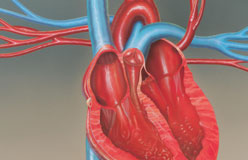
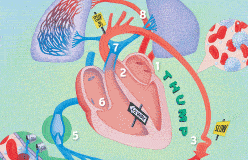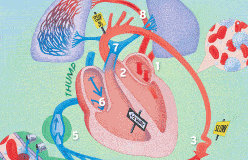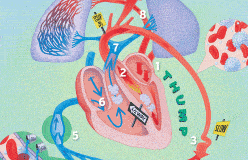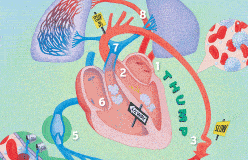
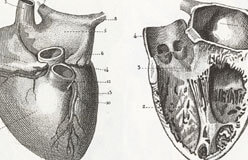
In medicine, keeping the heart beating is a top priority.
But that’s not a simple task, because so many things can go wrong. Diseases such as viruses can invade and destroy heart tissue. Globs of fat can block vessels. Mechanical parts can wear out, the muscle itself can weaken with age, and its built-in timer can misfire. What can modern medicine do to fix a broken heart? Mend it—sometimes.