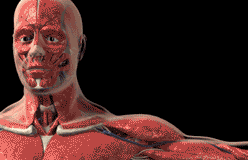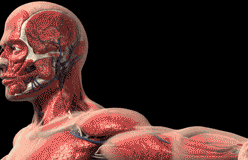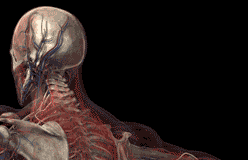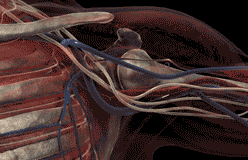
In 1664, English scientist Robert Hooke viewed a thin slice of cork through an early microscope. To him, it looked like it was made of many tiny rectangular chambers.
He called them cells, from the Latin word cella. That means “small room.”
At first, scientists couldn’t see much in a cell. They thought it was just filled with jelly. They called that jelly protoplasm. But microscopes got better, and that view changed. We know now that each cell is a complex part of life.