What makes you grow up to be tall or short, or have big or small bones? Your shape depends on the genes you get from your parents. But a star’s life is shaped by only one thing: how massive it is when it is born.
Stars with more mass burn hotter and brighter. They also burn out faster. So stars that keep cool live longer by burning slower. The hottest stars are blue. The coolest stars are red. Others are yellow, like our Sun. Most stars in our galaxy are red dwarfs. Here are some of the different kinds of stars.

◀ Brown Dwarfs
When is a star not a star? When it is too small to start its nuclear furnace but too big to be a planet. Astronomers call these objects brown dwarfs, or failed planets. They are scattered across the galaxy. So far, only eight planets have been found to orbit brown dwarfs. But these planets would be much too cold to support life as we know it. In this image, the brown dwarf is at the lower right. It is orbiting the bigger red dwarf in the center.
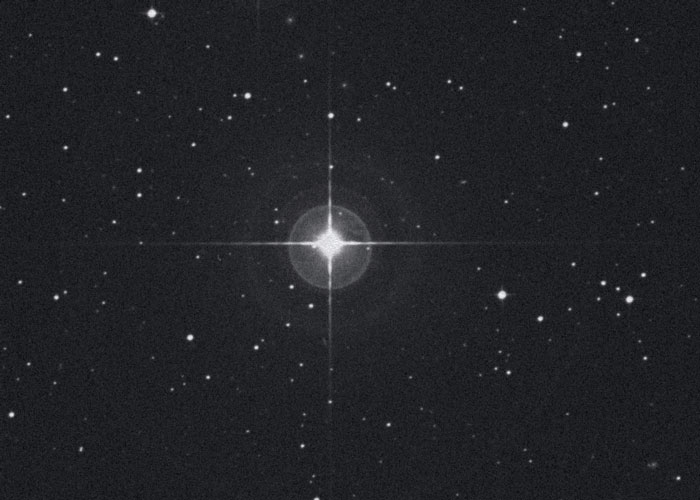

▲ Red Dwarfs
This star is Lacaille 8760. It is one of the biggest and brightest red dwarf stars known. The sky is covered with red dwarfs. But most aren’t bright enough to see without a telescope. It’s like looking at a lawn and knowing it is full of ants, but the ants are too small to see. Even though Lacaille 8760 is so big and bright, it can just barely be seen. Only someone with a very good eye under a black and clear sky can spot it.
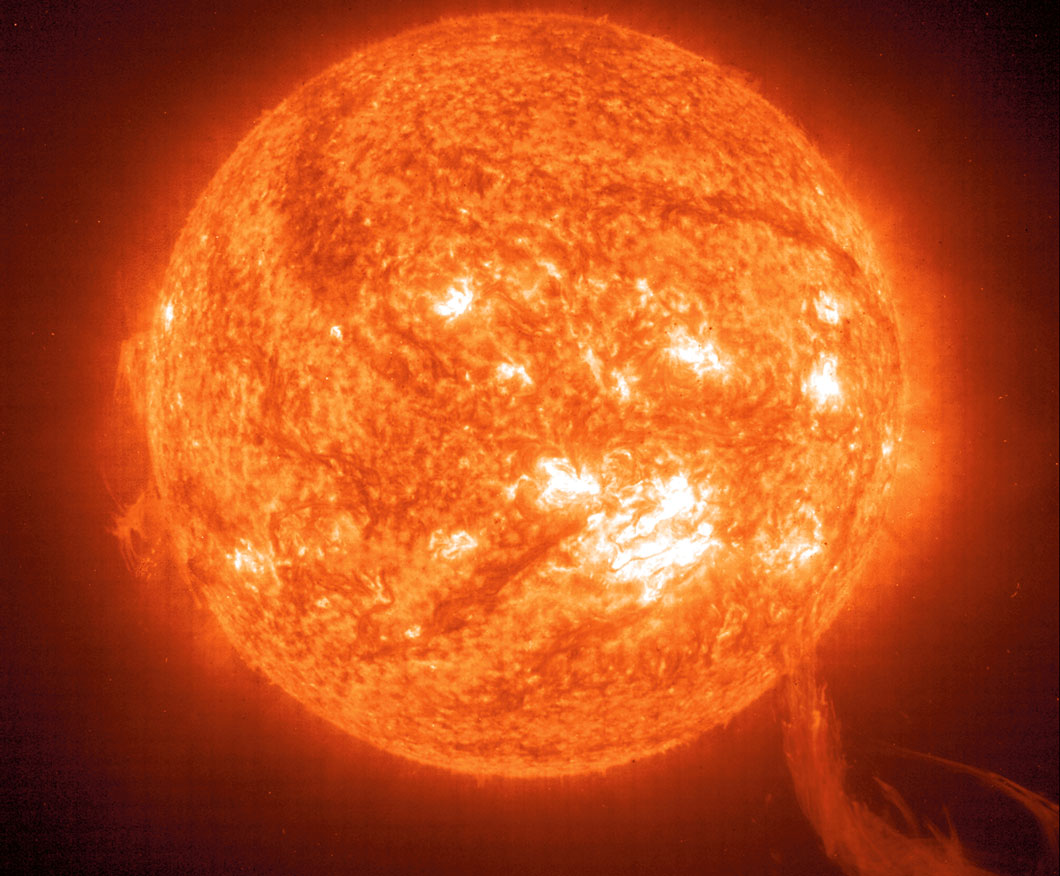

▲ Yellow Dwarfs
Our Sun is a yellow dwarf star. Its surface temperature is 11,000°F. Yellow dwarfs shine for 10 billion years before burning out. That makes them great hosts for a planet with life. Their own long life provides enough time for life to form, as it did on Earth over billions of years.
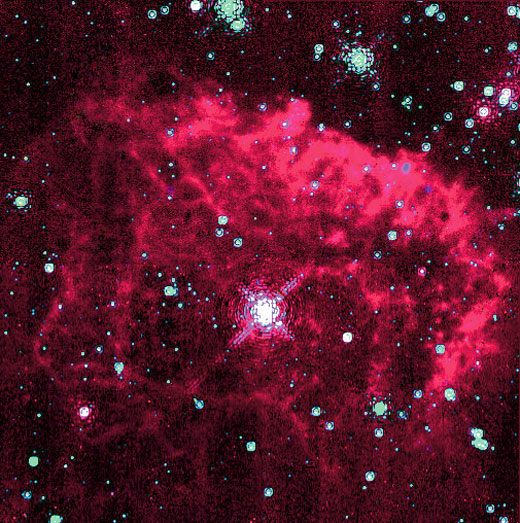

◀ Luminous Blue Variable Star
The brightest star in our galaxy is really, really far away. It’s so far away, it is hidden by the Milky Way’s dark dust clouds. This picture was taken in infrared light. It shows the star and its nebula. The star is nicknamed the Pistol Star. It is 10 million times brighter than our Sun and 150–250 times more massive. That’s about as big as a star can get!
Binary Star System
Blue-white Sirius is a large binary star system. Binary means it has two parts. Sirius is in the winter constellation Canis Major, the Great Dog. Sirius A (shown here) is the brightest star in the night sky. That’s mainly because it is nearby. It’s just 8.6 light-years away! It has a small companion called Sirius B. That’s a burned-out star called a white dwarf. ▶

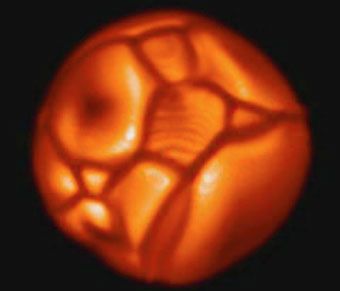
◀ Red Giants
Late in its life, a star swells up to many times its original size. That’s because its nuclear furnace is putting out a lot more energy. It makes the star blow up like a hot air balloon. The image shown here was created by a computer. It shows large cells and bright spots on a supergiant.







